Lyme illness was first recognized in 1975, in Lyme, Conn., however scientists nonetheless have extra questions than solutions about how the micro organism answerable for the situation that wreaks such havoc for some individuals, leaving them with debilitating signs for years, whereas inflicting comparatively gentle illness for others. Assessments for Lyme have excessive false damaging charges, particularly early within the an infection, so even detecting the illness is difficult.
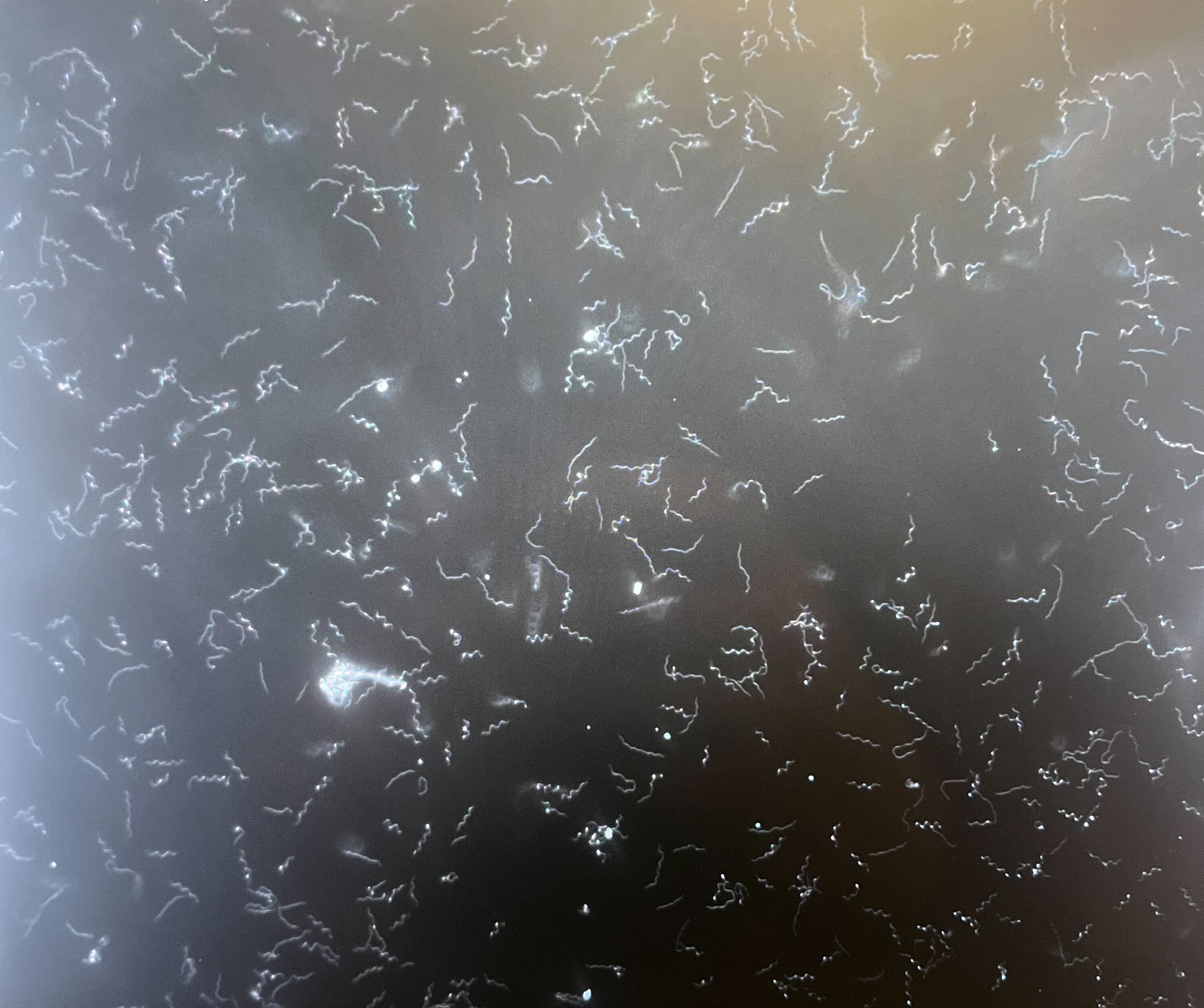
In a paper printed in PLOS Pathogens, a world group of researchers report on probably the most complete evaluation of the Borrelia burgdorferi genome up to now, which supplies clues about what’s inflicting extra extreme types of the illness, and lays the inspiration for growing higher diagnostic checks and coverings. The info come from samples painstakingly taken from 299 Lyme sufferers within the northeastern and midwestern U.S., and central Europe, principally extracted from pores and skin biopsies of the bullseye-shaped rashes which are an indicator early signal of an infection. The scientists first remoted the micro organism from the biopsied pores and skin samples, then correlated genetic signatures of the micro organism with the sufferers’ well being outcomes. That allowed them to establish genes that had been related to extra extreme signs in addition to perceive why U.S. sufferers are likely to have completely different signs than these in Europe.
“This info is foundational for growing diagnostics, vaccines, and therapies,” says Pardis Sabeti, from the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Massachusetts Common Hospital, and Harvard College, and a senior writer of the paper. “Realizing the genes which are there, we are able to begin seeing the variety that exists, and characterizing their perform. It’s just like the Human Genome Venture—this genetic info is what’s wanted earlier than we are able to even start to develop higher diagnostics and coverings.”
Within the paper, the scientists confirmed earlier, smaller genetic research of B. burgdorferi that correlated genetic markers on the bacterial genome to illness signs in individuals. They discovered particular genetic modifications related to extra extreme illness, which may sooner or later be used to find out whether or not a specific an infection entails a pressure of the micro organism that’s more likely to result in extra severe sickness.
Additionally they discovered particular proteins on the floor of the micro organism that had been related to the flexibility to unfold past the preliminary website of an infection (i.e. a tick chew) by way of the blood to have an effect on different tissues and organs. “That’s when a lot of the problematic elements of Lyme illness begins,” says Dr. Jacob Lemieux, from Massachusetts Common Hospital and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and first writer of the examine. “The micro organism might go to the nervous system, inflicting neurological Lyme illness, or if it goes to the joints, it might probably trigger Lyme arthritis. Dissemination is a watershed occasion as a result of it may imply the distinction between a gentle and extreme case.”
Whether or not these markers are additionally related to submit Lyme illness syndrome, wherein individuals proceed to expertise lingering signs months or years after their an infection, isn’t clear but. But it surely may assist to demystify what’s inflicting the syndrome. “Sufferers who’ve disseminated Lyme illness do have greater charges of submit Lyme illness syndrome,” says Lemieux. “We hypothesize that sure strains of Lyme usually tend to result in post-treatment Lyme syndrome, and we’d wish to establish what these strains are. So realizing which sufferers are contaminated with strains which are extra more likely to disseminate may assist us to review new therapeutics and interventions for submit Lyme syndrome.”
Learn extra: How Local weather Change Impacts the Unfold of Lyme Illness
By highlighting attainable genetic markers related to the micro organism’s potential to roam the physique after an infection, the scientists hope to catalyze extra analysis into testing and responding to those markers to scale back severe signs.
The intensive genetic info gathered on this examine additionally supplies clues about why individuals within the U.S. expertise completely different Lyme signs than these in Europe, and why checks within the U.S. might not detect infections picked up abroad. “We discovered that the genetics [of the bacterial strains] fluctuate by areas,” says Lemieux. Within the U.S., particularly within the northeastern elements of the nation, strains are typically extra invasive and disseminate by means of the physique after an infection, which may contribute to extra extreme illness. Variations of the micro organism extra frequent in Europe are likely to trigger power pores and skin situations and neurological signs,
“We’re solely scratching the floor of this,” says Lemieux of the information represented by this genetic database, which he and his workforce uploaded to the general public genetic analysis database GenBank, from the Nationwide Institutes of Well being, for different scientists to review and analyze. “This paper is one brick within the basis, and a invaluable software for the sphere.”
Extra Should-Reads From TIME