Last 12 months, instances of measles—a critical, vaccine-preventable illness that is extremely contagious—jumped by 79% world wide. Most of them had been in youngsters. That development is continuous this 12 months, threatening to reverse a powerful 73% drop in measles deaths worldwide from 2000 to 2018.
Circumstances within the U.S. are climbing, too. In simply the primary two months of 2024, 35 instances have already been reported in 15 states together with California, Minnesota, Florida, New York, and Louisiana; in 2023, 58 instances had been reported over all the 12 months.
Why are measles instances taking off, and the way can folks shield themselves?
Why measles instances are climbing
Not sufficient children are getting vaccinated. For herd immunity, about 95% or extra of a inhabitants must be vaccinated, however most nations world wide have been under that threshold for years. By 2019, 86% of children worldwide had been vaccinated with a dose by their second birthday, however that quantity dropped even additional to 81% in 2021. (The measles vaccine is given in two doses: one at a 12 months, the subsequent at age 4-6.)
Vaccination charges within the U.S. are declining, too, and vaccination exemption charges are creeping up. CDC knowledge present that 93% of kindergarteners had been vaccinated towards measles in the course of the 2021-22 college 12 months
Vaccinating extra youngsters is one of the simplest ways to stop new outbreaks. The vaccine, which has been round for the reason that 1960s, is given as a mixture shot that additionally consists of safety towards mumps and rubella. One dose is 93% efficient towards measles, and two doses are 97% efficient. “The science actually helps the protection and effectiveness of vaccinations,” says Dr. Katherine Baumgarten, medical director for an infection management and prevention at Ochsner Well being in New Orleans. Nevertheless, “we all know there’s numerous mistrust in vaccines, and that’s a disgrace. If vaccination charges proceed to say no, then we’ll see extra of the ailments that we had hoped to utterly remove.”
How measles spreads
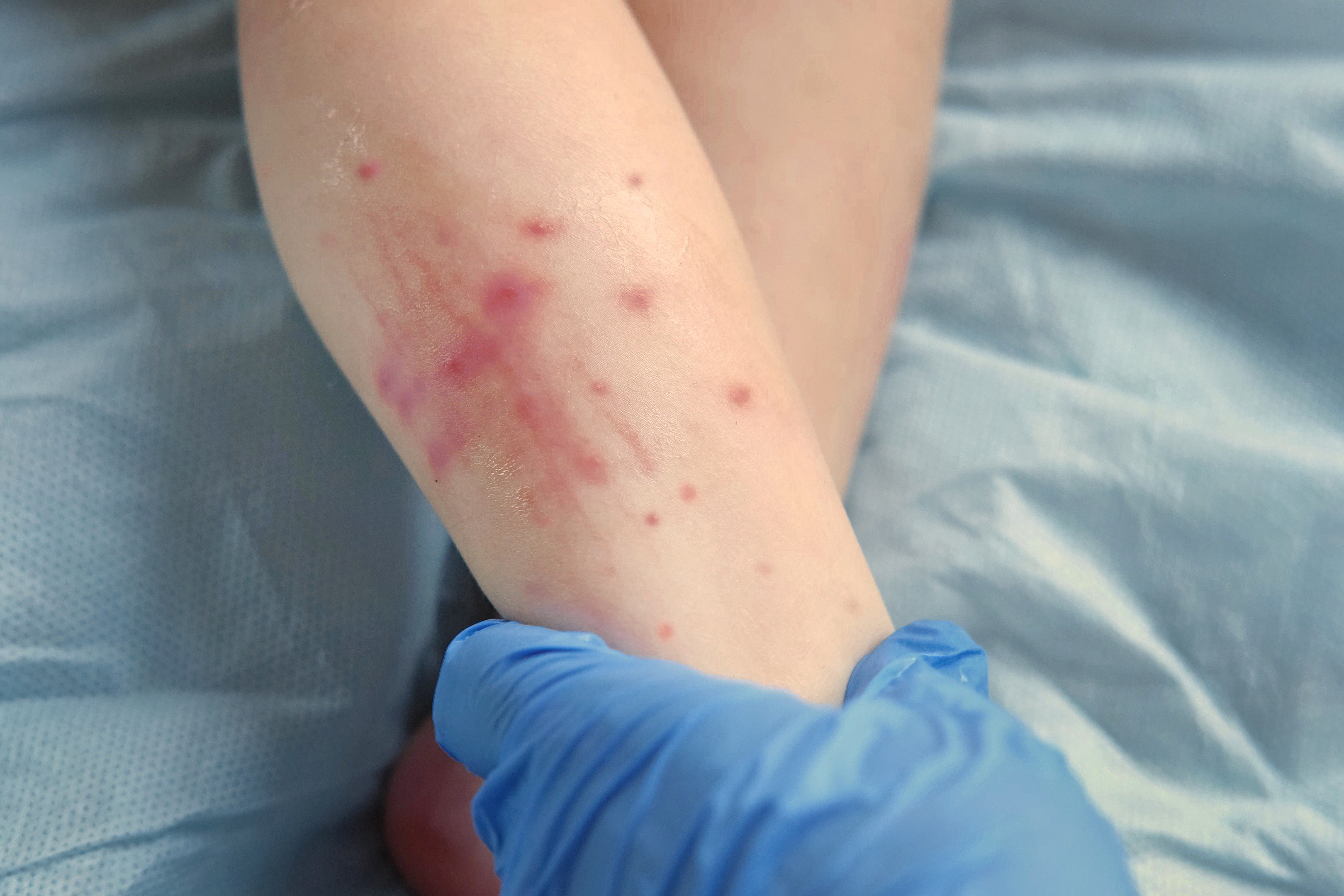
Measles is likely one of the most contagious ailments on the planet. It spreads via the air, by infectious droplets, and on surfaces. “If an individual has not been uncovered or vaccinated, then they typically get contaminated if they’re uncovered 90% of the time,” Baumgarten says. Measles may cause a rash, excessive fevers, and even mind swelling and loss of life.
Circumstances pose a specific menace to individuals who can’t get vaccinated, corresponding to infants lower than a 12 months outdated, individuals who have weakened immune methods on account of medical circumstances or transplant surgical procedures, and pregnant ladies—even when they have been vaccinated—since their immune methods are extra vulnerable whereas they’re anticipating. “If [people with measles] come to a health care provider of hospital for care and are in a ready room with different sufferers, they might expose different folks,” Baumgarten says.
Why fewer children are getting vaccinated
Rising vaccine-refusal is one cause. One other is COVID-19.
Measles instances had began climbing in 2019, however they dropped considerably in 2020, when a lot of the world went into lockdown and adopted stricter public well being prevention measures, corresponding to sporting masks and practising social distancing. These behaviors make it tougher for any virus, together with measles, to unfold. It’s additionally doable that following the surge in instances in 2019, extra of the world’s youngsters grew to become immune as a result of that they had contracted the an infection, and due to this fact fewer had been vulnerable to the illness.
However lockdowns additionally interrupted children’ vaccinations. As well being assets shifted to controlling the pandemic, vaccination packages world wide had been placed on maintain. The World Well being Group (WHO) estimates that 22 million youngsters missed the primary dose of their measles vaccine in 2022, almost definitely on account of disruption brought on by COVID-19.
Lots of these children nonetheless aren’t immunized. Some nations have strict packages for vaccinating children at particular ages, so if baby misses their window, they might discover it onerous to get immunized in a while. “We do have extra vulnerable youngsters globally, so outbreaks might get greater and extra frequent,” says Dr. William Moss, government director of the Worldwide Vaccine Entry Heart at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg Faculty of Public Well being. “For an outbreak, you want two issues: a vulnerable pool of individuals, principally youngsters, and introduction of the virus.”
Outbreaks are likely to originate elsewhere—however consultants are nonetheless nervous
There would not appear to be a reservoir of virus endemic to the U.S. that is seeding new instances. Most outbreaks in varied states begin when an individual contracts measles throughout journey, then returns residence.
However that state of affairs continues to be regarding, particularly for communities the place measles vaccination protection is decrease on account of rising anti-vaccine sentiment or non secular causes for avoiding immunizations. In these areas, a vulnerable inhabitants plus introduction of the measles virus might spawn a cluster of instances, Moss says.